The heat sink with clips is a very popular solution due to its simplicity. This system is “easy”, but presents many details we think it is important to know about.
The first element of this kind of product was presented in the United States in the late 80s; some years later, the original design was modified and brought to the European market by various companies.
This heat sink has, in addition to the fins, a flat face where the electronical element can be fixed. An innovative development came with the decision to use a clip to fix the electronical element instead of a regular screw.

The use of a clip has many advantages:
- The operation of mounting the electronic module is much more rapid with the clip than with a screw.
- The electronic module (TO220 or TO247) is pressed and fixed uniformly. This homogeneous contact between heat sink and electronical component improves thermal performance.
- The aluminum profile is cheaper as machine-threaded holes are avoided.
- The operator can assemble many modules at the same time; profiles can be placed on lines and the clips can be opened simultaneously.
- The risk of damage to the electronic element during mounting is far less than it would be if using a screw (which, if over-tightened, can crack the module).
This heat sink is composed of three main parts:
- Aluminum profile
- Clip
- Pin
The aluminum profile is an extruded bar that can, depending on the various producers, come in different shapes. This product can receive some superficial treatments:
- Anodization offers protection against corrosion, as well as better performance due to improved irradiation effect. It normally gives a dark color, although colorless anodization is also possible. The process of anodization has an electrical isolation effect.
- Surtec 650 is a chromium (VI)-free trivalent treatment which protects the heat sink from corrosion and maintains its electrical conductivity.
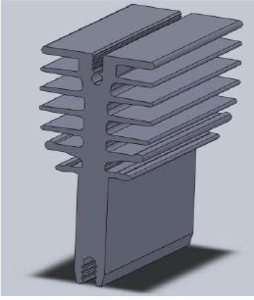
The clip is the defining element which sets this system apart. Clips can have different thicknesses, widths and different clamping forces, and can be classified by their corresponding component (TO220 or TO247).
The clamping force is determined by:
– The lever arm (distance between clip cave and point of contact with the module).
– The width of the clip (greater width = stronger clip).
– The thickness of the clip (greater thickness = higher pressure).
– The thickness of the module (as above).
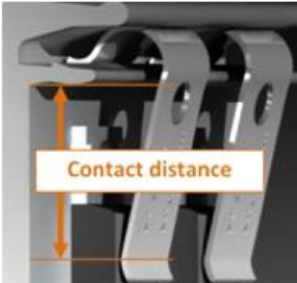
The clips were originally zinc-coated by some producers, but this treatment made them fragile, with the potential risk of breakages during the mounting phase or later. To avoid this inconvenience, the clips are now also nickel-plated. Some clips feature a hole to expedite the eventual module demounting; a pointed object can be used to lift the clip in order to remove the module.

The pins are used to connect the heat sink to the PC board. They can be pressed or screwed into the aluminum profile. The pins are characterized by a dimension called standoff. This is the distance between the heat sink and the board once mounted. The standoff space is usually 0, 2, 3 or 5mm. In the event of no standoff space (stand off = 0), the aluminum profile will be in direct contact with the board. The pins are usually soldered to the PC board.

As you can see, the heat sink with clips setup can save you time and money. Please don’t hesitate to contact us for available profiles or to improve your current system.
Click on the picture and download our free e-book
“Four Common Mistakes To Avoid When Selecting a Heat Sink”
